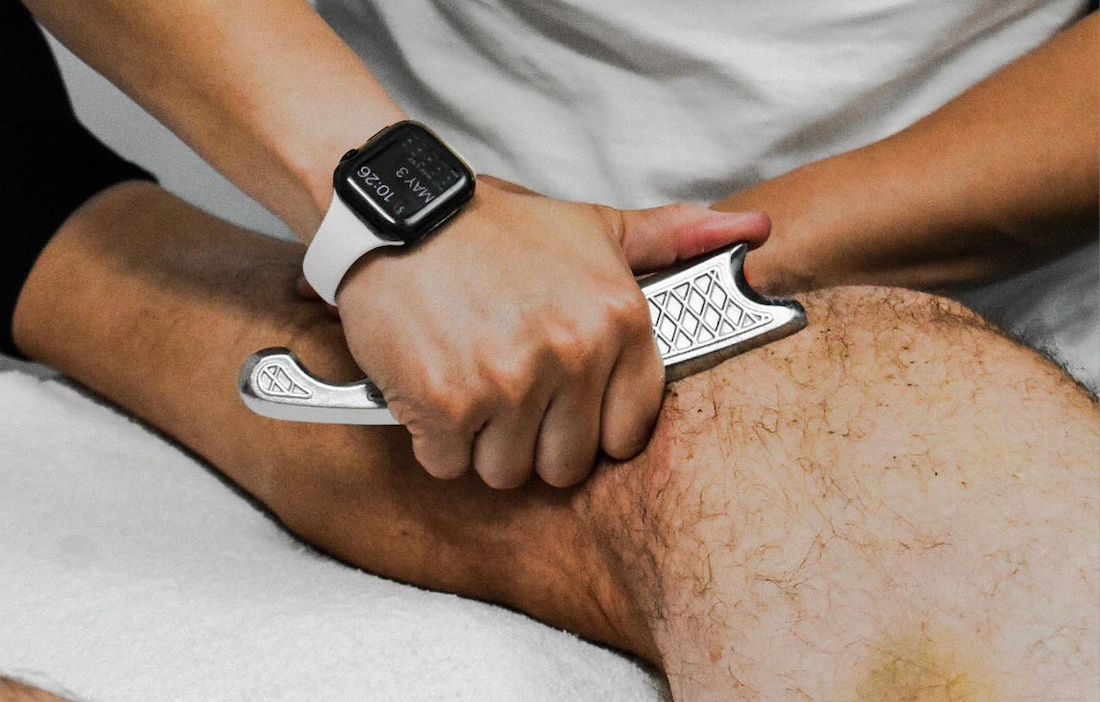
IASTM Explained
Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM) is a skilled manual therapy technique used to detect and treat soft tissue restrictions. Often called muscle scraping, it’s performed with specialized soft tissue mobilization tools designed to provide clinicians with enhanced tactile feedback and allow for targeted treatment. By gliding stainless steel instruments over the skin, practitioners can identify adhesions, scar tissue, and other restrictions, then apply controlled pressure to stimulate healing, improve mobility, and reduce pain.

HawkGrips has become a trusted leader in the IASTM community, providing both premium instruments and world-class education for clinicians. HawkGrips tools are precision-engineered for comfort, control, and durability, offering advantages in ergonomics, hygiene, and treatment efficiency.
In this article, we’re tackling nine of the most common misconceptions about IASTM, separating fact from fiction to give you a clear, evidence-based understanding of how this technique works.
Myth 1: IASTM doesn’t work– it’s just placebo
It’s true that some manual therapies rely heavily on the body’s perception of touch, which can raise questions about placebo effects. But Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM) has been studied extensively, and the results go beyond subjective reports of “feeling better.”
Multiple peer-reviewed studies show that IASTM can improve range of motion, reduce pain, and accelerate recovery after soft tissue injuries. Research has documented measurable increases in joint flexibility, decreases in pain scores, and faster return-to-play timelines in athletes following IASTM treatment compared to control groups.
One reason IASTM produces real, measurable changes is the tactile feedback the instruments provide to the clinician. The stainless steel tools amplify subtle textural differences in the soft tissue, allowing practitioners to detect adhesions, scar tissue, or fascial restrictions that may not be as easily identified by hand. This targeted approach means the treatment is not random — it’s highly specific, and that specificity is what helps drive results.
For those who want to explore the science for themselves, many of these findings are detailed in research such as:
-
Cheatham et al., 2016 – The efficacy of instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization; systematic review on improving soft tissue mobility and recovery.
- Laudner et al., 2014 – Acute effects of IASTM on range of motion in collegiate athletes.
- Doeringer et al., 2023 – Instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization increased hamstring mobility; randomized controlled study.
(Full research reference list available at the end of this article)
Myth 2: It’s the same as just using your hands
While skilled hands are the foundation of any manual therapy, IASTM tools, like HawkGrips’ stainless steel instruments, offer capabilities that fingers alone can’t match. The contoured edges, varied shapes, and weight distribution allow for greater precision, deeper tissue access, and more targeted detection of adhesions or restrictions.
Hands also fatigue quickly, especially for clinicians performing multiple treatments per day. Over time, this can contribute to strain injuries and shorten a practitioner’s career. HawkGrips’ ergonomic design and textured grip are specifically designed to be an extension of your hands, helping you deliver effective treatments while protecting your joints and muscles from overuse.
By reducing strain and amplifying tactile feedback, high-quality soft tissue mobilization tools allow clinicians to treat more patients effectively and comfortably, without sacrificing their own health in the process.
Myth 3: Why buy premium IASTM tools when I can just use a butter knife?
You don’t have to use a professional IASTM tool to perform soft tissue mobilization, but there’s a reason premium instruments exist. Professional-grade tools, like HawkGrips, are designed for hygiene, safety, precision, and durability. Stainless steel instruments are easy to clean, provide consistent pressure, and reduce the risk of infection…benefits that household items simply can’t match.
Beyond safety, purpose-built tools give clinicians stellar control and tactile feedback. Each contour, edge, and weight distribution is made to glide over soft tissue smoothly, detect adhesions, and allow precise treatment without overworking the clinician’s hands.
In short, while any flat surface could technically be used, high-quality IASTM tools make treatments safer, more effective, and more comfortable for both patients and clinicians. They’re the recommended choice for anyone serious about delivering the best care.
Myth 4: IASTM is too aggressive and damages tissue
Some people assume that IASTM therapy (or “muscle scraping”) is harsh on the body because they’ve seen images of post-treatment redness or bruising. In reality, when performed by a trained professional, IASTM is a controlled, safe, and evidence-based technique designed to activate the body’s natural healing response– not to cause harm.
Mild redness after treatment is a normal and temporary reaction, caused by increased blood flow to the area. It is not a sign of tissue damage. While some individuals may experience slight bruising, this is not required for the treatment to be effective, and it should never be the goal.
With proper training and the right tools, clinicians can adjust pressure, technique, and duration to match each patient’s needs — ensuring treatment remains both comfortable and therapeutic. HawkGrips’ design allows practitioners to work effectively while maintaining the gentle control needed for safe, healthy outcomes.
Myth 5: You need red marks or bruising for it to be effective
Following the misconception that IASTM treatment is “too aggressive,” another common myth is that visible bruising is proof the session worked. In reality, muscle scraping does not need to leave any marks to be effective.
Modern, evidence-based approaches to IASTM prioritize patient comfort and targeted tissue mobilization– not post-treatment discoloration. While some redness or light bruising can occur as a normal byproduct of increased circulation, the absence of marks does not mean the treatment failed.
Skilled clinicians use controlled pressure and targeted techniques to achieve results without unnecessary trauma to the tissue, with patient comfort and safety always at the forefront.
Myth 6: It’s Only for Elite Athletes
While IASTM gained some of its visibility through professional sports, these tools are not limited to elite athletes. Clinicians across healthcare settings, from major hospital systems to private practice PT clinics, use soft tissue mobilization tools with patients of all ages and activity levels.
IASTM is commonly applied in:
- Post-surgical recovery to reduce scar tissue and restore mobility
- Chronic pain management for conditions like tendinopathy or low back pain
- Everyday use by people recovering from injury, addressing nagging pain, or simply working to stay strong and active
IASTM techniques can even be adapted for specialized populations, such as pediatric and geriatric care, underscoring its versatility across patients of all ages.
In other words, IASTM isn’t reserved for athletes at the top of their game. It’s a versatile, evidence-based treatment that benefits anyone looking to move better and recover faster.
Myth 7: IASTM doesn’t help with muscle recovery
Some people think IASTM isn’t a true recovery tool– probably because they associate it only with treating injuries or breaking up scar tissue. But clinicians and athletes alike use Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization to speed recovery after workouts, practices, or competitions.
By improving blood flow, reducing adhesions, and stimulating tissue repair, IASTM supports faster recovery and helps muscles perform at their best. That’s why it’s become a go-to muscle recovery tool, often referred to as “muscle scraping,” for both athletes and everyday people.
Myth 8: IASTM only works on swelling
Some people think IASTM treatment is just for swelling… likely because early use in sports rehab often focused on acute injuries. In reality, Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization goes far beyond that. Clinicians use it to address scar tissue, chronic pain, tendon injuries, and mobility restrictions, among other things.
By targeting soft tissue adhesions and improving movement, IASTM helps patients recover more effectively and return to activity with less pain. Swelling relief can be a side benefit, but it’s far from the whole picture.
Myth 9: IASTM and the Graston Technique are interchangeable
While the terms often get mixed up, they’re not the same thing. Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM) is the therapeutic approach– a hands-on technique used by clinicians with specialized tools. The Graston Technique is a branded system created by the company Graston, which sells its own instruments and teaches courses under that name. Using the Graston Technique means following their specific tools, training, and protocols, but not all IASTM therapy is Graston.
Graston became widely known because it was one of the first companies to bring IASTM tools to market, not because it’s the only or best option. Think of it like saying “Kleenex” when you mean “tissue.” Kleenex is a brand, but tissues come in many forms. The same goes for IASTM tools– Graston is one brand and the Graston Technique is their system, while HawkGrips is another leading provider.
In short: Graston is a brand. IASTM is the therapy.
The Bottom Line on IASTM
Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM), often called muscle scraping, is far more than a passing trend. Backed by research and trusted by clinicians, IASTM is a proven and versatile therapy that supports recovery, reduces pain, and improves mobility. From scar tissue and chronic pain to sports performance and post-workout recovery, soft tissue mobilization tools like HawkGrips help patients and athletes alike reach their goals faster.
Ready to experience the difference? Explore our HawkGrips instruments and education programs to see how these tools can transform your treatment approach and results.
For More Reading on IASTM, check out this document of references.